Coarse Grained Movies in MATLAB
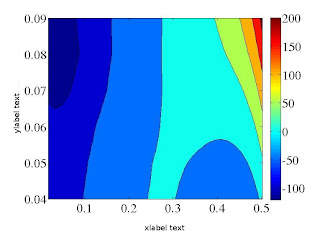
AIM : Let say the aim is to prepare a movie of coarse grained description of the system. In this example the 2-dimensionl lattice has been divided into several sub-square lattices. Then depending on the order parameter values (average) in the sub-square lattices, the color has been chosen and finally each frame has been added using 'addframe'. clear all; close all; aviobj = avifile('box_movie.avi','compression','None'); aviobj.KeyFramePerSec = 1; fig = figure; fid = fopen('fort.214'); nbox = 25; nframes = 9900; for i = 1:1:nframes A = fscanf(fid, '%g', [1 nbox]); if (i < 3500) && (mod(i,5) == 0) % Draw smaller boxes xstart = 0; ystart = 0; xlen = 1; ylen = 1; rectangle('position', [xstart, ystart, xlen, ylen]); nx = floor(sqrt(nbox)); ny = nx; ...